Japan is accelerating the deployment of offshore wind power, and one of the most symbolic projects in this effort is the Murakami Tainai Offshore Wind Power Project. This initiative is part of the Japanese government’s second round of offshore wind power auctions—commonly known as “Round 2”—and represents a critical step toward achieving the national targets of 10 GW of offshore wind capacity by 2030 and 30–45 GW by 2040.
With a total planned capacity of 684 MW, the project will significantly contribute to the decarbonization of Japan’s energy mix through fixed-bottom offshore wind power. It is also expected to drive regional industrial development and economic revitalization. This article provides a detailed overview of the project, including its schedule, estimated CAPEX & OPEX and evaluation based on investment viability.
Project Overview
| Project name | Murakami Tainai Offshore Wind |
| Developer | Murakami Tainai Offshore Wind Consortium |
| Consortium Members | Mitsui & Co., Ltd. RWE Offshore Wind Japan Murakami-Tainai K.K. Osaka Gas Co., Ltd. |
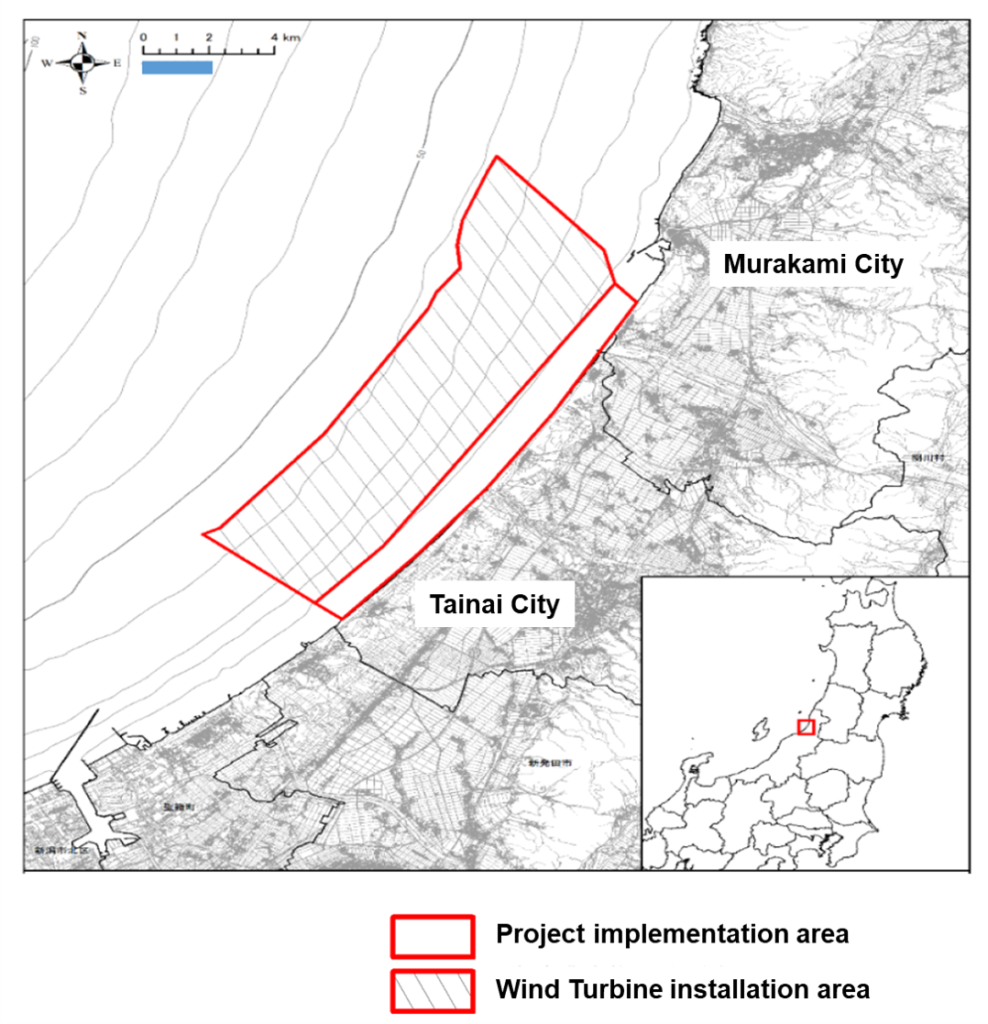
| Location | Offshore murakami and tainai City, nigata Prefecture |
| Type | Fixed-bottom Offshore Wind Power |
| WTG | GE |
| Price | 3 JPY/kWh |
| Capacity | 684 MW (18 MW × 38 turbines) |
| Start of Construction | april 2025 |
| Operation Period | june 2029 –2054 |
Location
Consortium Members
Mitsui & Co., Ltd.
- A general trading company founded in 1876.
- Engaged in a wide range of business sectors, including steel products, mineral and metal resources, energy, infrastructure projects, transportation, food, retail, healthcare, and ICT. Actively investing in renewable energy businesses as well.
RWE
- Started its power generation business in Germany in 1898.
- Holds a total generation capacity of 39.3 GW, including 3.5 GW in offshore wind—ranking second globally in offshore wind capacity.
Osaka Gas Co., Ltd.
- Launched operations in 1905. Supplies city gas to approximately 5 million customers, mainly in the Kansai region (2 prefectures and 5 districts).
- Its core businesses include “Domestic Energy (Gas & Electricity),” “Overseas Energy,” and “Life & Business Solutions.”
- Contributes to a low- and decarbonized society through integrated operations, from renewable energy development to supply (serving 1.71 million low-voltage customers).
Project Implementation Structure
Construction Phase
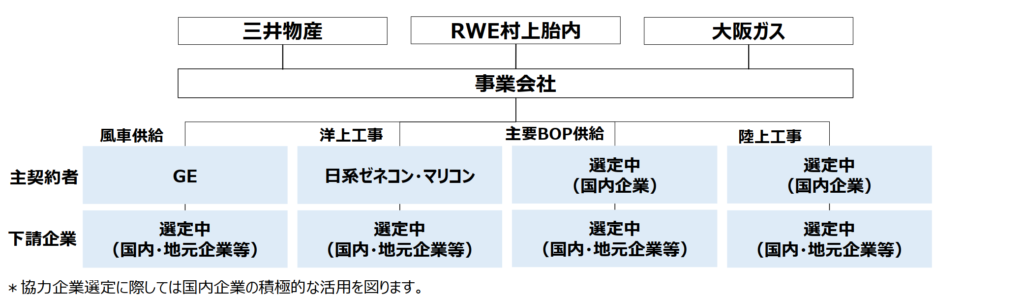
Source: Public document by the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, METI
Operation Phase

Source: Public document by the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, METI
Project Timeline
Development & Design Phase (2023–2025)
- December 2023: Award of public auction
- Environmental impact assessment, wind condition, wave, and seabed geological surveys
- Local stakeholder consultations and coordination
- Wind farm certification and submission of construction plan
Construction Phase (2025–2029)
- April 2025: Construction of onshore substation and transmission infrastructure
- June 2027: Installation of offshore foundations and cables
- November 2028: Assembly and installation of wind turbines
Operation & Maintenance Phase (2029–2054)
- Turbine maintenance: GE
- Operation management (BOP): RWE
Decommissioning & Repowering Phase (Post-2054)
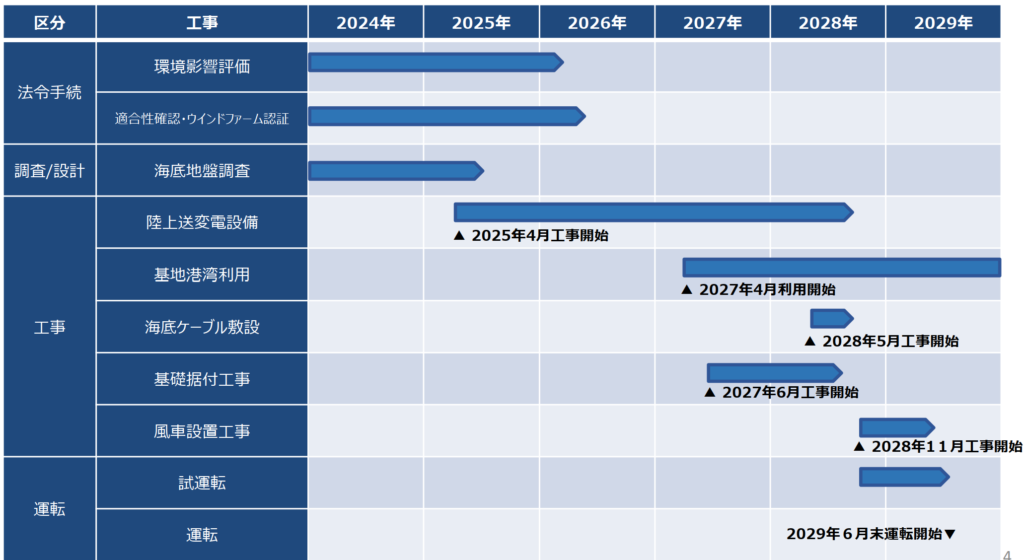
Source: Public document by the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, METI
CAPEX & OPEX Estimates
Capital expenditures (CAPEX) and operational expenditures (OPEX) were estimated with reference to NEDO’s offshore wind cost model as of October 2024.
The estimated capital expenditure (CAPEX) for the Murakami Tainai Offshore Wind Power Project is approx. ¥282 billion , with long-term operational costs (OPEX) projected at approx. ¥4.8 billion annually.
📌 CAPEX Breakdown for 684 MW:
| CAPEX Breakdown | Estimated Cost (Billion JPY) |
|---|---|
| Turbine Procurement | 155 |
| Foundation & Installation | 107 |
| Substations & Grid Connection | 20 |
| Total | 282 |
Evaluation based on investment viability
We estimated the annual energy production (AEP) using estimated power curves and wind condition data from NEDO’s NeoWins. And we calculated IRR (internal rate of return) and LCOE (levelized cost of energy), which are commonly used indicators for investment evaluation. In addition, we evaluated the competitiveness based on investment viability by using our original evaluation criteria. The following assumptions were applied:
- WACC (weighted average cost of capital): 6.5%
- Operational period of the wind farm: 25 years
- Power selling price: ¥18/kWh
| Promotion Zone | Rated Power | Gross Capacity Factor | Net Capacity Factor (with loss) | AEP (kWh) | CAPEX (¥ billion) | OPEX (¥ billion) | IRR (%) | LCOE (¥/kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murakami Tainai Offshore Wind | 18 MW | 33.27% | 26.62% | 1594788134 | 282 | 4.8 | 6.86 | 17.5 |
Evaluation Criteria
| Rating | IRR | LCOE | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| ★★★★★ Very Promising | ≥ 9.5 % | ≤ 15 ¥/kWh | Both investment viability and power generation efficiency are exceptionally high. A zone that should be given top priority. |
| ☆☆☆☆ Promising | 8–9.5 % | 15–17 ¥/kWh | High investment potential; profitability is achievable depending on other factors such as port and grid infrastructure. |
| ☆☆☆ Neutral | 6.5–8 % | 17–19 ¥/kWh | Potentially viable depending on conditions. Cost reductions and support measures will be key. |
| ☆☆ Challenging | 5–6.5 % | 19–22 ¥/kWh | Profitability is somewhat low and would require technical and regulatory support as a prerequisite. |
| ☆ Unprofitable | < 5 % | > 22 ¥/kWh | Currently challenging. Fundamental regulatory support or technological innovation is necessary. |
Evaluation Result
| Promotion Zone | Rating |
|---|---|
| Murakami Tainai Offshore Wind Power Project | ☆☆☆ Neutral |
Summary
Murakami Tainai Offshore Wind Power Project represents a significant milestone in Japan’s push for renewable energy. According to the analysis for competitiveness based on investment viability by J-WIND Times, the evaluation result is “Neutral”. Potentially viable depending on conditions. Cost reductions and support measures will be key.
Conclusion
Murakami Tainai Offshore Wind Power Project represents a significant milestone in Japan’s push for renewable energy. With a strong focus on sustainability, economic development, and technological innovation, it lays the foundation for the expansion of offshore wind power in Japan.
📚 Want to dive deeper? Explore J-WIND Times’ featured categories!
🔍 Market Trends & Analysis – Stay ahead with insights into the latest developments shaping renewable energy investments.
🏛 Policy & Regulation – From auction schemes to FIP reform, get a clear understanding of Japan’s evolving energy rules.
⚙️ Projects – Discover the progress and behind-the-scenes of offshore wind projects across Japan.
💡 Technology & Innovation – From next-gen turbines to floating foundations, explore the cutting edge of offshore wind tech.



